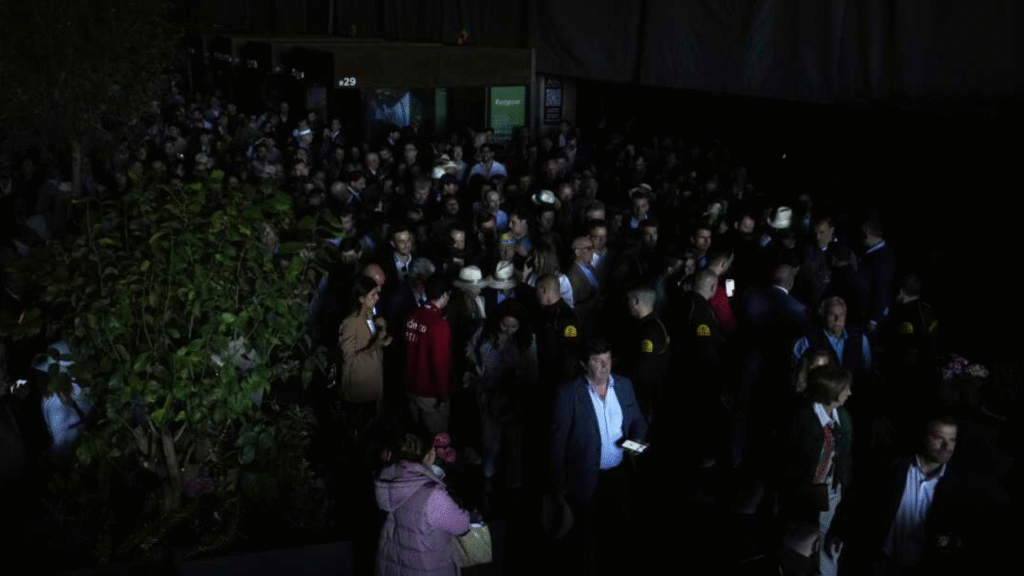
The Spain-Portugal blackout of April 2025 stunned millions across the Iberian Peninsula. A sudden voltage surge triggered one of the largest power outages Europe had seen in decades, affecting over 60 million people. From homes plunged into darkness to halted public transport and closed businesses, the blackout exposed vulnerabilities in modern power grids. In this article, we explore the causes, consequences, and lessons learned from this unprecedented event.

The Day the Lights Went Out
On April 28, 2025, residents of Spain and Portugal woke up to an unexpected reality: the entire electrical system was compromised. Cities that never sleep were suddenly silent. Hospitals operated on backup generators, airports delayed flights, and public transport came to a halt. For hours, millions wondered what caused such widespread disruption.
Investigations revealed the Spain-Portugal blackout was not due to human error or cyberattacks. Instead, the culprit was a cascading voltage surge. This surge originated from a sudden shutdown of renewable energy sources, which triggered a chain reaction in the Iberian grid.
What Caused the Voltage Surge?
Understanding the Cascade Effect
The Iberian electricity network is closely connected to the wider European grid. When a large power source suddenly goes offline, it creates an imbalance between supply and demand. In this case, the abrupt shutdown of several solar and wind farms caused a loss of synchronization with the continental grid. The system struggled to stabilize voltage, leading to a cascading failure.
Contributing Factors
Several factors worsened the situation:
- Overreliance on Renewable Energy: Rapid integration of solar and wind energy outpaced infrastructure upgrades.
- Insufficient Backup from Thermal Plants: Conventional plants could not compensate quickly for lost renewable generation.
- Aging Grid Components: Certain transmission lines lacked advanced voltage control systems.
This combination created a perfect storm for the Spain-Portugal blackout, showing that modern grids must balance innovation with reliability.
Immediate Impact of the Blackout
Daily Life Disruptions
Millions were directly affected. Traffic lights went out, causing chaos in city centers. Retail stores and supermarkets shut down. Communication networks experienced temporary outages. Even routine tasks like cooking, working from home, or attending school were interrupted.
Economic Consequences
The blackout also had a severe economic impact. Industries reliant on continuous power faced losses, especially in manufacturing and technology sectors. Some estimates suggested the financial toll ran into billions of euros.
Public Safety and Healthcare
Hospitals switched to emergency power, but the strain on critical systems highlighted the risks associated with large-scale outages. Emergency services were stretched thin, and vulnerable populations faced significant challenges.
Lessons from the Iberian Blackout
The Spain-Portugal blackout serves as a wake-up call for grid operators and policymakers. Here are key takeaways:
1. Grid Modernization is Crucial
Investments in smart grid technology can prevent cascading failures. Real-time monitoring, automated controls, and advanced voltage stabilization are essential to handle sudden power surges.
2. Diversification of Energy Sources
While renewable energy is critical for sustainability, it must be complemented by reliable conventional sources to maintain balance during emergencies.
3. Emergency Preparedness and Public Awareness
Governments and utility companies should educate the public on how to respond during power outages. Simple measures, like having backup power for essential devices, can save lives.
Case Study: Successful Grid Stabilization in Germany
In contrast, Germany’s 2024 grid experienced a similar renewable-related imbalance but avoided a blackout. Investments in real-time grid monitoring and hybrid energy sources allowed operators to stabilize voltage before cascading failures occurred. This example highlights the importance of foresight and technological upgrades to prevent disasters like the Spain-Portugal blackout.
Strategies to Prevent Future Blackouts
Enhancing Grid Resilience
- Automated Voltage Controls: Advanced sensors can detect voltage irregularities and adjust flows instantly.
- Energy Storage Systems: Large-scale batteries can provide backup power during sudden losses.
- Load Balancing: Smart systems can reduce strain by shifting energy demand to less congested areas.
Tips for Individuals and Businesses
- Invest in Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Critical for home offices and small businesses.
- Plan Emergency Kits: Include flashlights, batteries, and essential medical supplies.
- Educate Staff and Family: Make sure everyone knows safety protocols during a blackout.
FAQs About the Spain-Portugal Blackout
Q1: What caused the Spain-Portugal blackout?
The blackout was triggered by a cascading voltage surge, caused by sudden shutdowns in renewable energy sources and grid synchronization failures.
Q2: How many people were affected by the blackout?
Over 60 million residents in Spain and Portugal experienced power outages during the incident.
Q3: Could the blackout have been prevented?
Yes, with better grid infrastructure, automated voltage control systems, and sufficient backup power from conventional sources.
Q4: What lessons can other countries learn from this event?
The key lesson is that renewable integration must be paired with smart grid technologies and emergency preparedness to prevent cascading failures.
Q5: Are blackouts like this common in Europe?
No, the Iberian blackout was one of the largest in decades. Europe generally maintains reliable grids, but this incident underscores the need for modernization.
Conclusion
The Spain-Portugal blackout revealed the fragility of modern power systems under stress. A sudden voltage surge caused widespread disruption, affecting millions and highlighting vulnerabilities in grid infrastructure. While renewable energy is vital for a sustainable future, it must be supported by robust systems and backup measures. By investing in smart grids, diversified energy sources, and public awareness, nations can prevent similar blackouts and ensure reliable power for all. The Iberian blackout is a lesson in preparedness, technology, and the delicate balance of modern energy systems.





